The Impact of the Coronavirus on the Global Supply Chain
China plays a crucial role in the global supply chain,and the impact from the novel coronavirus epidemic will be felt worldwide. So far it is not entirely clear how long I will take to control the outbreak so it is hard to gauge the extent of the impact. But this is already having a substantial impact on global financial markets which perceive a previously underestimated threat to the real economy. The following is a look at how the outbreak could affect China's foreign trade and the global supply chain.
How long the coronavirus epidemic lasts and which nations are hard hit will determine the extent of the impact on the global supply chain. The consequences will also vary from one industry to another. Should there be a serious outbreak in key economies outside China,the shock will certainly intensify. Already South Korea,Japan,Italy and Iran are struggling to contain a serious challenge. Some 50 countries have been affected,most of them to lesser extents.
The outbreak has already affected production in China and that will hit foreign trade. In turn that will have an impact on the global supply chain. The epidemic has caused businesses to delay their work resumption after the Spring Festival holiday. Lockdowns have disrupted travel so many migrant workers have been unable to get back to work after returning home for the holiday. The disruptions to the flow of people (including cross-border mobility) and domestic quarantines will affect production and operation of enterprises,which in turn,will affect China's imports and exports. Cross-border movements of goods and services enable the global supply chain to bind nations together. With greater integration of economies around the world,disruptions are also greater.
Migrant Workers Stranded
But let's look at various possibilities. Assume that the baseline scenario is there is no greater outbreak domestically,under which the business resumption ratio is 100%. This ratio directly affects China's imports and exports. If the business resumption rate declines by 50%,China's import and export volume will also fall 50% compared to that in the baseline scenario. Since the pneumonia outbreak caught wide attention right before the Spring Festival (January 25),and the following six days are China's official holiday,we would assume that in January,the epidemic has caused no major impact on China's economy or the global supply chain. However,the impact in February has already been evident. Based on this,the author has established two scenarios: the first scenario is a more optimistic one. In this scenario,the resumption ratio in February is one-third. That means that in March all businesses resume normal operation.
The second scenario presumes a more severe situation,in which the resumption ratio is only 20% in February,followed by 80% in March,and 100% in April. Both scenarios assume that the impact on China's economy is limited to the first quarter.
After the 2008 financial crisis,global foreign trade rebounded rapidly between 2009 and 2011,and China was no exception. But since 2012,the nation's economy has entered a prolonged downturn. Therefore,for China's foreign trade,it is more reasonable to take the average performance from 2012 to 2019 as the baseline scenario (without the outbreak of the epidemic). The quantitative analysis made on account of this baseline scenario shows that the growth of China's exports and imports will be 7.82% and 5.17%,respectively,in February,3.89% and 1.89% in March and 4.53% and 3.15% for the first quarter. The growth in exports and imports for all of 2020 will be 3.67% and 2.69%,respectively.
Generally speaking,the epidemic's impact on China's foreign trade will be very severe in February and significant over the first quarter. The figures for the whole year will also be affected although the impact will diminish over time. The business resumption ratio will ultimately be evident in foreign trade. In the above scenario,China's exports and imports will fall 71.88 and 70.12 percentage points respectively in February,17.64 and 19.38 in the first quarter,and 3.89 and 4.47 in the whole year.
In the second scenario,which assumes the epidemic to be more severe,the exports and imports will decline by 86.26 and 84.14 percentage points respectively in February,20.78 and 20.38 percentage points in March,28.63 and 30.35 in the first quarter,and 6.32 and 6.99 percentage points for the whole year. It is very clear that China's foreign trade will be severely affected by the epidemic in February,which in turn will further influence the result for the first quarter. When measured over the course of the whole year,the impact on foreign trade is still quite big,the pace of economic growth will slow,and exports will encounter negative growth for the first time in the last four years.
Nonetheless,the final outcome will be tolerable in economic terms. In the first scenario,the growth rate of China's exports and imports in 2020 will be -0.22% and -1.78%,respectively,and -2.65% and -4.30% in the second scenario. Despite the influence of the epidemic,both scenarios show that the growth rate of China's exports and imports will not be significantly lower than that of 2019,which were 0.50% and -2.70%,respectively. Looking back,we will find that the situation was even worse in 2015 and 2016. The growth rate for China’s exports and imports were respectively -2.94% and -14.27% in 2015,and -7.73% and -5.46% in 2016. As China withstood heavy downward pressure at that time,we have every reason to trust our country will be able to overcome the difficulties we are facing now.
China is an integrated part of the global supply chain. In 2015,China's exports and imports of intermediate goods already accounted for 53.05% and 79.49% of the nation's total exports and imports,respectively. Thus,the author believes that the epidemic will certainly deliver a significant shock to the global supply chain though this should be mainly reflected in the first quarter data.
Result Varies Across Industries
There are two ways the epidemic will impact the global supply chain via China's foreign trade. One is that it affects China's production and exports,which in turn cuts into China's demand for imported intermediate goods. The other is that it hampers China's production and exports of intermediate goods to other regions. That in turn affects the production of the importing nations.
We can easily understand the country-specific influence of the epidemic simply by looking at the ranking of China's top trading partners. According to 2019 data,China's top five trade partners were the European Union,which accounted for 15.41%of China's foreign trade,followed by ASEAN with 14.02%,the United States with 11.83%,Japan 6.88% and South Korea 6.22%. Taken together they are more than half of the nation's trade. Therefore,it is clear that all of the world's three major regional supply chains - the Asian supply chain,the European supply chain and the North American supply chain -- will be affected to some extent.
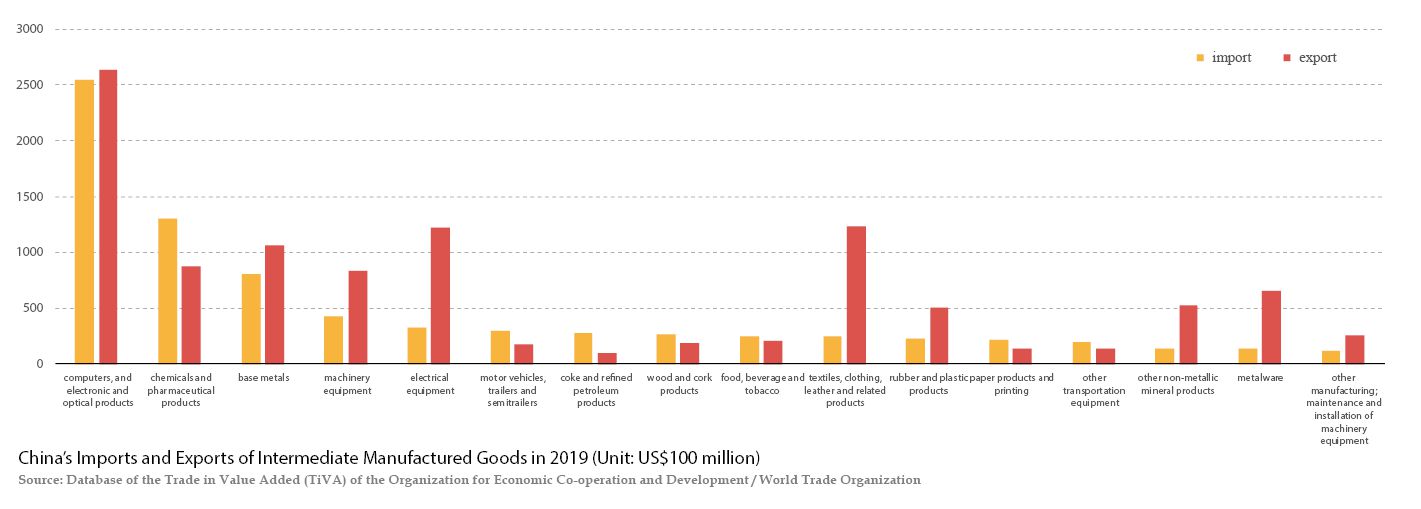
The hardest-hit sectors will be computers,electronics and optical products. Both the import and export shares of intermediate goods in these three sectors are much higher than in other sectors. The figures from last year were a combined 32.89% and 24.57% for imports and exports,respectively. Since China plays an important role in the global supply chain in these sectors,the epidemic will have a significant impact. Machinery equipment,electrical equipment,base metals,chemicals and pharmaceutical products will also be affected,but the surge in demand for pharmaceutical products due to the epidemic itself will cushion the negative impact on that industry. In addition,as the second-largest intermediates export sector in China,the supply suspension in the textiles,clothing,leather and related products industries will also affect the global supply chain.
Need for Further Examination
The outbreak in Hubei province and its capital Wuhan will affect the domestic supply chain but a lesser impact on the global supply chain but have a lesser impact on the global supply chain. Wuhan and the rest of Hubei province have strictly limited inflows and outflows of people. As a result,the greatest impact will be felt there. However,the import and export volume of Hubei was US$57.1 billion dollars in 2019,accounting for only 1.25% of the country's total. The import and export volume of Wuhan customs also only accounted for 0.72% of the total volume of all customs areas in China,so the impact will be quite limited. But it is worth noting that,the crude steel production of Hubei was 30.74 million tons in 2018,ranking it seventh nationally and accounting for 3.31% of China's total. And the provincial output of 2.4194 million automobiles also ranked fourth nationally,accounting for 8.7% of China's total. That means the epidemic in Hubei will inflict serious damage to these two sectors and certain enterprises in these industries. But the impact globally in these sectors will not be that severe.
The second matter is what impact the coronavirus outbreak in South Korea and Japan will have on the global supply chain. South Korea has the most known cases of coronavirus outside China and its car production has already been affected. The impact on Japan's industrial sectors will depend on the severity of the outbreak. Japan is the third largest economy in the world,and it stays in the upstream position in the global supply chain. A wider spreading of the epidemic in Japan would lead to business shocks,which will undoubtedly cause severe shock to the global supply chain. If the outbreak is kept under control in Japan,there will be little additional harm to the global supply chain. Meanwhile,Hong Kong is an important hub for China's transshipment trade,accounting for 6.29% of the mainland’s total. There are concerns that the outbreak in Hong Kong could also have a further impact on global supplies.
The next matter is the follow-up impact of the outbreak. Its direct impact in the first quarter of 2020 should be our main focus,but we need to watch for signs of an impact that extends beyond this period. If relevant vaccines and treatments cannot be successfully developed,the epidemic might be controlled but not eliminated. That could mean another outbreak at some point,causing more victims and disrupting production.
The last matter of concern is whether the outbreak will lead to the migration of China's industrial chain. US Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross said that the outbreak in China will encourage companies to bring their factories back from China to the US. Others have stated that the coronavirus outbreak highlights the vulnerability of the global supply chain,which they say is too dependent on China.
Sino-US economic and trade friction is already affecting the development of China's industrial chain. The US has made a fundamental shift in its attitude towards China,and the epidemic has raised concerns that it will accelerate China's industrial chain migration. Nevertheless,the author believes that,unlike the trade friction and the attitude change of the US side toward China,the coronavirus outbreak is only a one-time event. Its impact will be short-lived. Once it is controlled or eliminated,business investments and foreign trade transactions will gradually recover. Pent-up demand could even lead to a sharp rebound at some point. Hence,the likelihood that the coronavirus will permanently damage China's industrial chain is limited.
The author is the deputy director and associate researcher of the International Trade Office at the Institute of World Economics and Politics,the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences





